Launching a Superior Reverse Transcriptase in a Commoditized Market: A Case Study
A Case Study on how to use an analytical approach to developing a commercialization strategy.
Introducing a new product into a well-established and highly commoditized market presents significant challenges. In today's intricate global landscape, simply offering marginally better performance at a slightly lower price is insufficient for success. To thrive, companies must strategically identify high-value market segments and applications, and efficiently reach their target users.
This case study explores how a startup can effectively launch a superior reverse transcriptase, dubbed RT-X, in a market dominated by commodity products.
Executive Summary
This case study explores how a startup can effectively launch a superior reverse transcriptase, dubbed RT-X, in a market dominated by commodity products. By conducting a comprehensive market analysis, the startup identified high-value market segments and applications where RT-X's superior performance can deliver significant value. The analysis included assessing the competitive landscape, developing a pricing model, and creating a targeted commercial strategy. The key findings and recommendations are:
Focus on the life sciences tools market, specifically NGS, gene expression, gene editing, and transcriptomics applications.
RT-X is differentiated by its high processivity, enabling it to work with more challenging samples and longer templates.
Implement a single pricing model with volume-based discounts, with recommended price ranges of $7-$9 per reaction for RT-X reagent-only and $8-$10 for cDNA synthesis kits.
Execute a 4-prong commercial strategy: direct US sales, global distribution, co-marketing partnerships, and OEM deals in sequencing.
This data-driven approach will enable the successful launch of RT-X despite the competitive market dynamics.
Market Analysis
To formulate a successful go-to-market strategy, a comprehensive understanding of the market, high-value applications, and competitive landscape is crucial. By conducting thorough market research, the startup can identify untapped opportunities and niche segments where RT-X's superior performance can deliver significant value to users. This analysis should include:
Identifying key market segments and their specific needs
Determining applications and use cases, where RT-X's superior performance can make a substantial impact
Assessing the competitive landscape and benchmarking RT-X against existing products
Developing a pricing competitive model that maximizes margins and top-line growth
Creating a commercial strategy that leverages direct sales and cultivates high-value partnerships
Market Segments & High-Value Applications
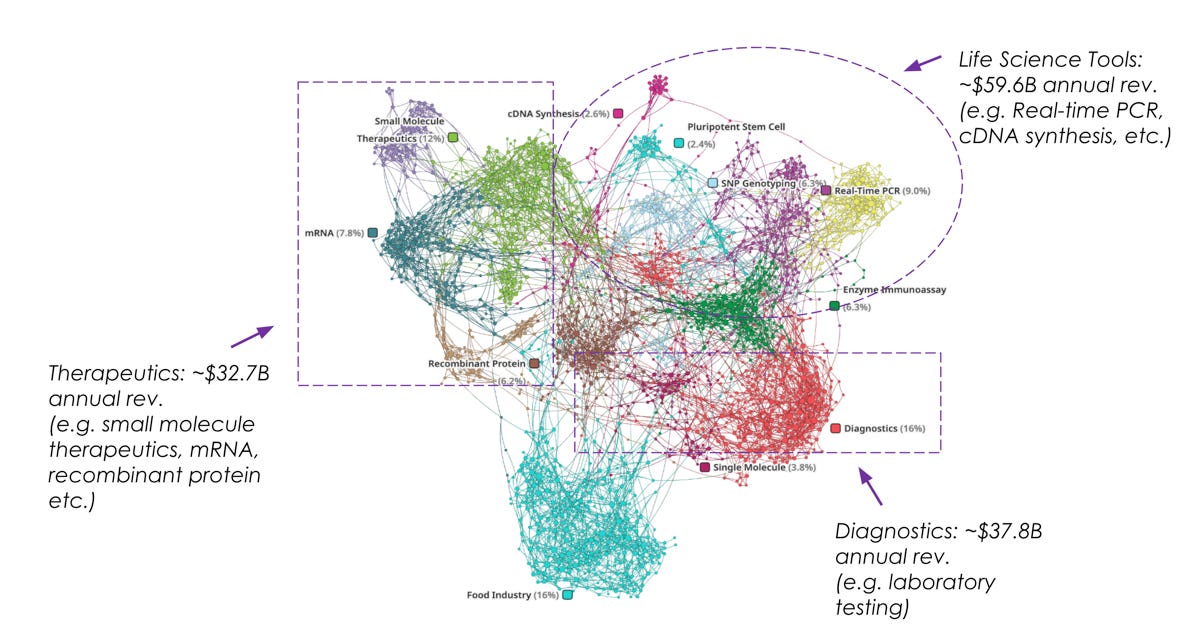
Network analysis1 combined with advanced natural language processing can be used to analyze thousands of publicly available articles related to reverse transcriptase. The network surfaces four distinct addressable market clusters (represented by tightly clustered colored dots in the network) with significant revenue potential - life sciences tools, diagnostics, therapeutics, and the food industry.
Each market segment has unique requirements and specific needs that should be considered to assess whether the start-up can immediately serve or should take a long-term position with market development. Within each market segment, certain applications should also be analyzed to identify where RT-X can deliver immediate and long-term value.
Considering the organization’s limited reach and resources, life sciences tools would be the lowest-hanging fruit as generating data in this segment can make a strong case for adoption in the diagnostic and therapeutic markets. Let’s focus this analysis to examine the life sciences tools segment and NGS, gene expression, gene editing, and transcriptomics applications.
Usage & Interest
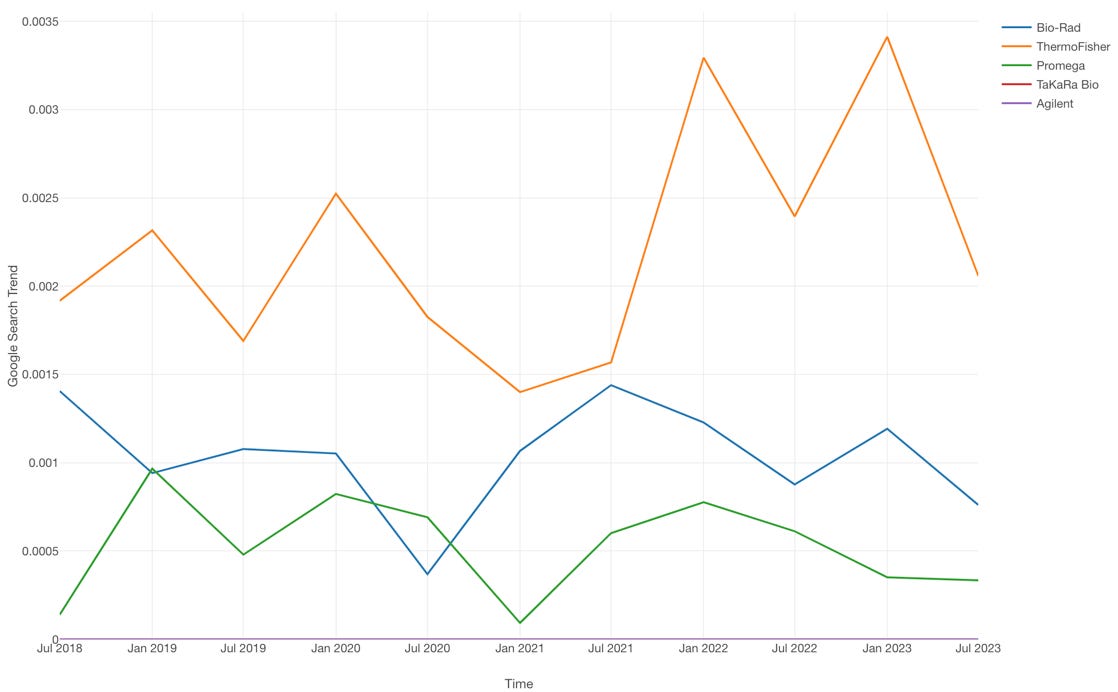
To better understand each application, we can analyze the US and worldwide Google Trends2 as a proxy for usage and interest in the market.
A 5-year Google Trends data for US shows gene expression and gene editing among high-interest applications. Transcriptomics (and spatial transcriptomics) is trending up over time while RT-PCR is seeing a decline. Note, the sharp sharp spike in RT-PCR is likely related to its utility in SARS-CoV2 diagnostic application during the 2019 pandemic. This data suggests certain applications are relatively more popular than others; therefore, we can build a tailored messaging and support data for RT-X to win in these areas.
Next, this data was used to generate a correlation matrix to understand the relationship between each application and RT.
The heatmap highlights a strong positive relationship between reverse transcriptase and gene editing, and to a lesser yet significant extend with RNAseq and transcriptomics. This suggests that usage and interest between these applications are related and can be complementary to each other. As such, the start up can focus on these high-demand and connected areas in the short term while cultivating interest in the others in the long term.
There is a wealth of other information that can be extracted from this correlation matrix. For example, RT-PCR is inversely correlated with almost all of the other applications, which may suggest usage and interest patterns are opposing with each other. This could be because users who are interested in RT-PCR do not search for the other categories because they have different profiles of interest and needs. This could help with refining the messaging and developing the right target customer profile for RT-X.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
Next, an in-depth analysis of 13 competitors (27 products) examining features, specifications, target markets, and pricing presents a highly commoditized market with mostly on-par specifications (data not shown). From a wide termostable range to low bias and high sensitivity, the product specifications are generally comparable with minor differences around the niche they serve (e.g. low input, template length, etc.). Since RT-X has high processivity, it stands out to have a higher dynamic range for working with more difficult use cases such as longer templates and challenging samples such as FFPE. Nonetheless, this new product needs to compete in a highly competitive market, where price and performance are tightly managed. This market is still growing due to the fierce innovation in the applications it supports but approaching maturity as it has been long integrated into core molecular biology techniques.
Another look at the 5-year US and worldwide (data not shown) to assess interest as a proxy for market share identifies ThermoFisher SuperScript IV as the 5-year market leader, followed by BioRad, Promega, and Agilent. TaKaRa, a niche offering, and others did not show significant interest. This data suggests RT-X will heavily compete with these companies that also serve its target applications in sequencing, gene expression, and gene editing.
Pricing Analysis
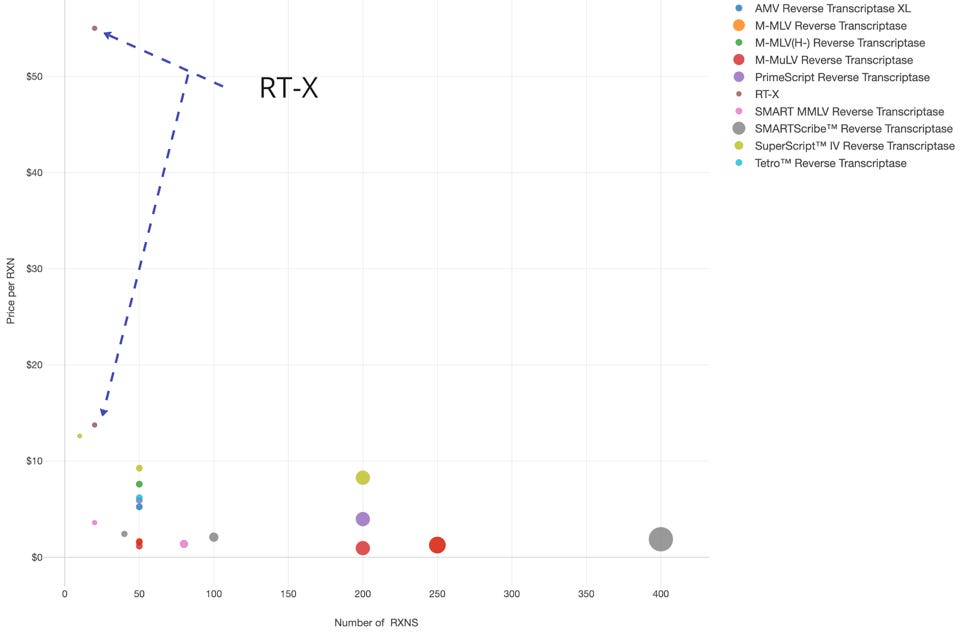
Now, lets look at the competitor pricing to inform how RT-X can be priced to maximize its position. The company hypothesized setting two different pricing, one for its for-profit client base and one for nonprofit clients. A pricing comparison was performed for 9 key competitors of RT-X.
The dot plot below shows tight clusters of price/reaction at common kit sizes of 50 and 200 reaction size kits. Interestingly, RT-X’s for-profit pricing is significantly higher than the market leader, SuperScript IV, while the non-profit pricing is slightly higher. This could present a couple of issues for the new contender though it is not without its benefits.
Pros:
Allows the company to support academic research and other non-profit work by offering more affordable pricing, which can generate goodwill and positive brand perception in the scientific community.
Charging higher prices to for-profit customers like biotech and pharmaceutical companies allows the company to capture more value from organizations with bigger budgets and commercial applications.
Cons:
In a highly commoditized market with many competitors, for-profit customers may simply choose the lowest price options if the company's for-profit price is not competitive. Brand loyalty tends to be lower in commoditized markets.
There could be challenges in clearly defining and enforcing the for-profit vs. non-profit distinction. Some organizations may span both categories.
Charging different prices for the same product risks frustrating for-profit customers who may feel they are unfairly subsidizing the lower non-profit pricing.
This approach can signal a deep discount range in high-volume scenarios such as OEM that can complicate negotiations.
Operationally, having two pricing tiers adds complexity in terms of accounting, sales, and customer account management compared to one uniform price.
As such, the recommendation would be to offer a single pricing model with the ability to receive volume-based discounts.
The company has an opportunity to offer a cDNA synthesis kit with RT-X inside. Let’s look at the price per reaction distribution across several competitors. The data shows a range of $2-$12 per reaction with the majority falling at around $6-$8 per reaction.
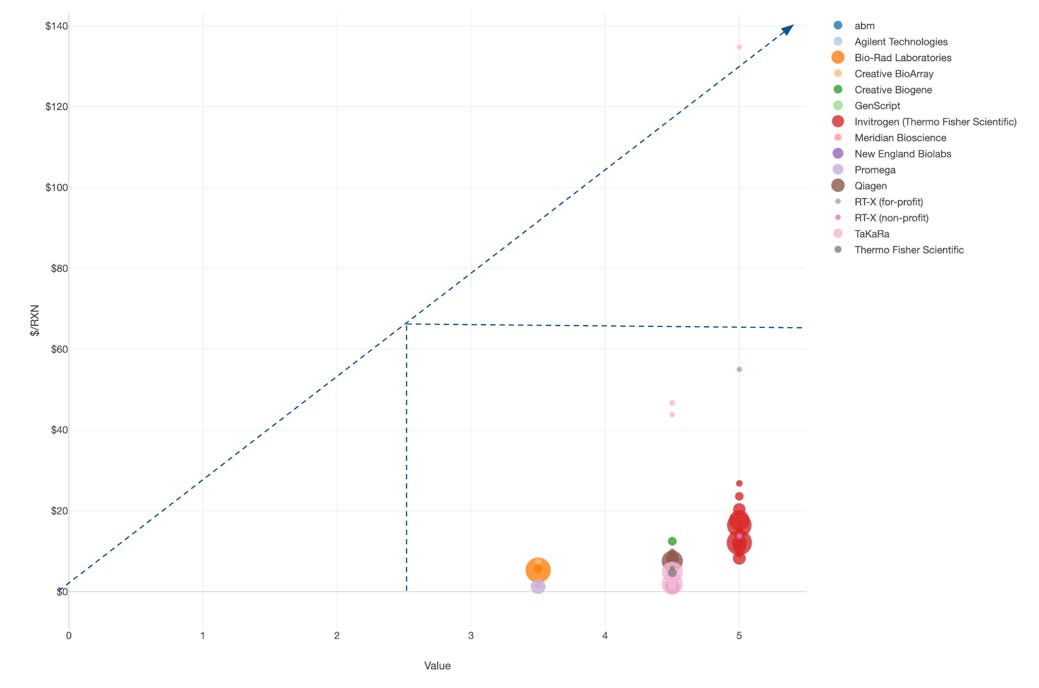
Additionally, a Price Value Map can help assess the current price and value positioning for commercially available RT and cDNA Synthesis Kits. This can further inform the best pricing range for RT-X to claim the position for a highly performant budget friendly product line.
As anticipated for a mature market, most products cluster in the high value at bargain pricing (bottom right), except TaKaRa’s SMARTer Pico PCR cDNA Synthesis Kit is an outlier in the high value at over market rate.
This suggests the current market is competitively priced and displacing the market leaders require more value delivered at a lower price.
This comparison reveals that RT-X's for-profit pricing is significantly higher than the market leader, SuperScript IV, while the non-profit pricing is slightly higher, pointing to price reduction being necessary to compete.
Price adjustment recommendation:
RT-X reagent-only at $7-$9 per reaction
RT-X cDNA synthesis kit at ~$8-$10
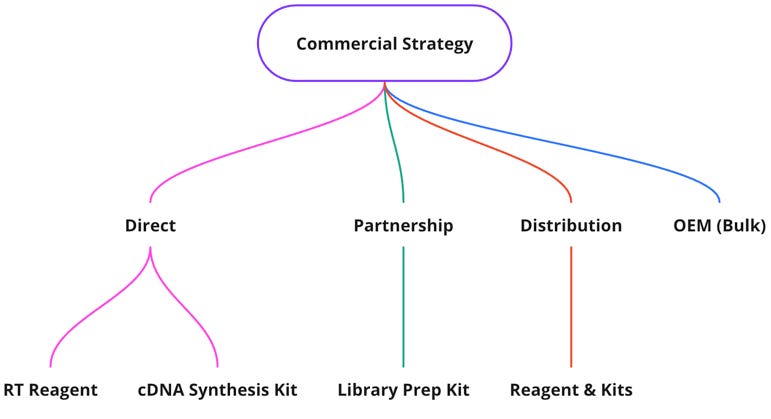
Commercial Strategy
Informed by our analysis, a 4-prong commercial strategy spanning two product configurations, direct and distributed business development, and forging strategic alliances can help expand the company’s reach and maximize revenue.
Direct sales in the United States targeting life sciences tools in gene expression, gene editing and transcriptomics.
Leverage digital marketing, webinars, and conferences to generate leads
Provide exceptional technical support to build customer loyalty
Global distribution with a 15-20% discount off list price for reagent-only and cDNA synthesis kits.
Prioritize key markets in Europe and Asia-Pacific
Recruit experienced distributors with existing life science customer base
Co-marketing partnerships to accelerate expansion into the sequencing segment.
Target library prep and end-to-end NGS providers
Jointly promote custom library prep kits featuring RT-X
OEM deals with major sequencing players
Integrate RT-X into their workflows as the recommended RT enzyme
Explore opportunities in spatial transcriptomics and single-cell sequencing
Conclusion
By developing a targeted go-to-market strategy focusing on high-value applications and market segments, supported by a data-driven understanding of the competitive landscape and pricing dynamics, the startup can effectively launch RT-X and gain share in a competitive market. The differentiated performance of RT-X, combined with strategic partnerships and focused commercial execution, will drive adoption and revenue growth. This analytical approach to product commercialization provides a strong foundation for success.
As always, feel free to reach out to me via email to discuss how these analysis strategies can support your business.
Cheers,
Mida